The Delhi Metro is a metro system serving Delhi and its satellite cities of Faridabad, Gurgaon, Noida and Ghaziabad in the National Capital Region of India. Delhi Metro Rail Corporation Limited (DMRC), a state-owned company with equal equity participation from the Government of India and the Government of Delhi, built and operates the Delhi Metro. It is the second oldest metro in India after the Kolkata Metro.
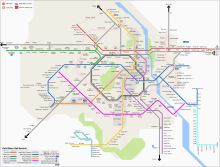
The Delhi Metro is the world’s 12th longest metro system in length and 16th largest in ridership. A member of CoMET,[5] the network consists of seven colour-coded regular lines and the faster Airport Express line, with a total length of 252 kilometres (157 mi) serving 185 stations (including 6 on Airport Express line).[1][6] The system has a mix of underground, at-grade, and elevated stations using both broad-gauge and standard-gauge. The power output is supplied by 25-kilovolt, 50-hertz alternating current through overhead catenary. The trains are usually of four, six, and eight-coach length.[1] DMRC operates over 3,000 trips daily, with first trains starting at around 05:00 and last at 23:30.[7] In the financial year 2016–17, the Delhi Metro had an average daily ridership of 2.76 million passengers and served 100 crore (1.0 billion) riders in total during the year.[3]
The Delhi Metro Rail Corporation was certified by the United Nations in 2011 as the first metro rail and rail-based system in the world to get “carbon credits for reducing greenhouse gas emissions” and helping in reducing pollution levels in the city by 630,000 tonnes every year.[1]
Planning for the metro started in 1984 when the Delhi Development Authority and the Urban Arts Commission came up with a proposal for developing a multi-modal transport system for the city. Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) was incorporated in May 1995, construction started in 1998, and the first section, on the Red Line, opened in 2002.[8] The development of the network was divided into phases, Phase I containing 3 lines was completed by 2006, and Phase II in 2011. Phase III is scheduled for completion by 2018 (originally planned for 2016).
The Rapid Metro Gurgaon which opened in 2013, whilst linked to Delhi Metro by the Yellow Line is a separate metro system (with a different owner/operator from the Delhi Metro), although tokens from the Delhi Metro can be used on its network.
Contents
[hide]
History[edit]
Background[edit]
The concept of a mass rapid transit for New Delhi first emerged from a traffic and travel characteristics study which was carried out in the city in 1969.[9] Over the next several years, many official committees by a variety of Government departments were commissioned to examine issues related to technology, route alignment, and Governmental jurisdiction.[10] In 1984, the Urban Arts Commission came up with a proposal for developing a multi-modal transport system, which would consist of constructing three underground mass rapid transit corridors as well augmenting the city’s existing suburban railway and road transport networks.[11]
While extensive technical studies and the raising of finance for the project were in progress, the city expanded significantly resulting in a twofold rise in population and a fivefold rise in the number of vehicles between 1981 and 1998.[11] Consequently, traffic congestion and pollution soared, as an increasing number of commuters took to private vehicles with the existing bus system unable to bear the load.[9] An attempt at privatising the bus transport system in 1992 merely compounded the problem, with inexperienced operators plying poorly maintained, noisy and polluting buses on lengthy routes, resulting in long waiting times, unreliable service, extreme overcrowding, unqualified drivers, speeding and reckless driving.[12] To rectify the situation, the Government of India and the Government of Delhi jointly set up a company called the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC) on 3 May 1995, with E. Sreedharan as the managing director.[13] Dr. E. Sreedharan handed over the charge as Managing Director of DMRC to Mangu Singh on 31 December 2011.
Construction[edit]
Physical construction work on the Delhi Metro started on 1 October 1998.[14] After the previous problems experienced by the Kolkata Metro, which was badly delayed and 12 times over budget due to “political meddling, technical problems and bureaucratic delays”, DMRC is a special-purpose organisation vested with great autonomy and powers to execute this gigantic project involving many technical complexities, under a difficult urban environment and within a very limited time frame. DMRC was given full powers to hire people, decide on tenders and control funds.[15] The DMRC then consulted the Hong Kong MTRC on rapid transit operation and construction techniques.[16] As a result, construction proceeded smoothly, except for one major disagreement in 2000, where the Ministry of Railways forced the system to use broad gauge despite the DMRC’s preference for standard gauge.[17]
The first line of the Delhi Metro, the Red Line, was inaugurated by Atal Bihari Vajpayee, the Prime Minister of India, on 24 December 2002.[18] The Delhi Metro became the second underground rapid transit system in India, after the Kolkata Metro, when the Vishwa Vidyalaya–Kashmere Gate section of the Yellow Line opened on 20 December 2004.[19] The first phase of the project was eventually completed in 2006,[20][21] on budget and almost three years ahead of schedule, an achievement described by Business Week as “nothing short of a miracle”.[22]
Construction accidents[edit]
On 19 October 2008, a launching gantry and a part of the overhead Blue Line extension under construction in Laxmi Nagar, East Delhi, collapsed and fell on passing vehicles underneath. Workers were using a crane to lift a 400-tonne concrete span of the bridge when the gantry collapsed along with a 34-metre-long (112 ft) span of the bridge on top of a Blueline bus, killing the driver and a labourer.[23]
On 12 July 2009, a section of a bridge collapsed while it was being erected at Zamrudpur, near East of Kailash, on the Central Secretariat – Badarpur corridor. Six people died and 15 were injured.[24] The following day, on 13 July 2009, a crane that was removing the debris collapsed, and with a bowling pin effect collapsed two other nearby cranes, injuring six.[25] On 22 July 2009, a worker at Ashok Park Metro station was killed when a steel beam fell on him.[26] Over a hundred people, including 93 workers, have died since work on the metro began in 1998.[27]
On 23 April 2018, Five people were injured when an iron girder fell off the elevated section of a Metro rail structure being constructed at the Mohan Nagar intersection in Ghaziabad. A car, an auto rickshaw and a motorbike were also damaged in the accident.[28]
Network[edit]
The Delhi Metro is being built in phases. Phase I completed 58 stations and 65.0 km (40.4 mi) of route length,[29] of which 13.0 km (8.1 mi) is underground and 52.1 km (32.4 mi) surface or elevated.[citation needed] The inauguration of the Dwarka–Barakhamba Road corridor of the Blue Line marked the completion of Phase I in October 2006.[30] Phase II of the network comprises 124.6 km (77.4 mi) of route length and 85 stations,[29] and is fully completed, with the first section opened in June 2008 and the last line opened in August 2011.[31] Phase III (103 km, 69 stations) and Phase IV (113.2 km) are planned to be completed by December 2018 and 2022 respectively.[citation needed]
Current routes[edit]
Phase I and Phase II[edit]
Phase I and Phase II routes and stations opened progressively from 5 December 2002 and 3 June 2008 respectively, and become completely operational on 11 November 2006 and 27 August 2011 respectively.
- Phase I:
A total of 65 kilometres (40 mi) long network with 58 stations and the following 3 routes (initial parts of Red, Yellow and Blue lines) were built within the limits of Delhi state, stations progressively started to open from 25 December 2002 to 11 November 2006.- Red Line, Line No.1:
Shahdara-Tri Nagar-Rithala, 22.06 kilometres (13.71 mi) route with 18 stations progressively started to open from 25 December 2002 to 1 April 2004. - Yellow Line, Line No.2:
Vishwa Vidyalaya-Central Secretariat, 10.84 kilometres (6.74 mi) route with 10 stations progressively started to open from 20 December 2004 to 3 July 2005. - Blue Line, Line No.3:
Indraprastha-Barakhamba Road-Dwarka Sub City, 32.10 kilometres (19.95 mi) route with 30 stations progressively started to open from December 2005 to 11 November 2006.
- Red Line, Line No.1:
- Phase II:
A total of 124.63 kilometres (77.44 mi) long network with 85 stations and the following 10 new routes and extensions was built, out of which seven routes are extension spurs of the Phase I network, three were new colour-coded lines and three routes connect to other cities (Yellow Line to Gurgaon, Blue Line to Noida and Blue Line to Ghaziabad) of the national capital region, outside the physical limits of Delhi state, in the states of Haryana and Uttar Pradesh. At the end of Phases I and II, the cumulative total length of the network became 189.63 km with 143 stations progressively becoming operational from 3 June 2008 to 27 August 2011.[1][32]- Red Line, Shahdara – Dilshad Garden:
3.09 kilometres (1.92 mi) route with 3 stations, an extension of Phase I, Line 1 became operational on 3 June 2008. - Yellow Line, Vishwavidyalaya – Jahangir Puri:
6.36 kilometres (3.95 mi) route with 5 stations, an extension of Phase I, Line 2 became operational on 3 February 2009. - Yellow Line, Central Secretariat – HUDA City Centre:
27.45 kilometres (17.06 mi) route with 19 stations, an extension of Phase I, Line 2 progressively became operational from 21 June 2010 to 3 September 2010, connects to Gurgaon in Haryana state with an interchange with Rapid Metro Gurgaon at Sikandarpur. - Blue Line, Indraprastha – Noida Sector 32 City Centre:
15.07 kilometres (9.36 mi) route with 11 stations, an extension of Phase I, Line 3 progressively became operational from 10 May 2009 to 13 November 2009, connects to Noida in Gautam Buddh Nagar district of Uttar Pradesh state. - Blue Line, Yamuna Bank – Anand Vihar ISBT:
6.17 kilometres (3.83 mi) route with 5 stations became operational on 27 January 2010. - Blue Line, Anand Vihar – KB Vaishali:
2.57 kilometres (1.60 mi) route with 2 stations became operational on 27 January 2010, connects to Ghaziabad district of Uttar Pradesh state. - Blue Line, Dwarka Sector 9 to Dwarka Sector 21:
2.76 kilometres (1.71 mi) route with 2 stations, an extension of Phase I, Line 3 became operational on 30 October 2010. - Orange Line, Airport Express Line:
22.70 kilometres (14.11 mi) route with 6 stations became operational on 23 February 2011. - Violet Line, Kashmiri Gate – Badarpur:
20.04 kilometres (12.45 mi) route with 16 stations progressively became operational from 3 October 2010 to 14 January 2011, its Phase III extensions to Mandi House and Faridabad became operational on 28 June 2014 and 6 September 2015 respectively. - Green Line, Inderlok – Kirti Nagar – Mundka:
18.46 kilometres (11.47 mi) route with 16 stations became operational on 27 August 2011.
- Red Line, Shahdara – Dilshad Garden:
| Line | First operational | Last extension | Stations[32] | Length (km)[33] |
Terminals | Rolling stock | Track gauge (mm) |
Power | Average Frequency(Minutes) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Line (Line 01) | 2002-12-24 | 2008-06-04 | 21 | 25.09 | Dilshad Garden | Rithala | 31 trains | 1676 | 25 kV OHE | 5 |
| Yellow Line (Line 02) | 2004-12-20 | 2015-11-10 | 37 | 49.31 | Samaypur Badli | HUDA City Centre | 60 trains | 1676 | 25 kV OHE | 5 |
| Blue Line (Line 03) Blue Line (Line 04) | 2005-12-31 | 2010-10-30 | 44 | 49.84 | Noida City Centre | Dwarka Sector 21 | 70 trains | 1676 | 25 kV OHE | 55 |
| 2010-01-07 | 2011-07-14 | 8 | 8.74 | Yamuna Bank | Vaishali | 1676 | 25 kV OHE | |||
| Green Line (Line 05) | 2010-04-03 | — | 14 | 15.14 | Inderlok | Mundka | 16 trains | 1435 | 25 kV OHE | 55 |
| 2011-08-27 | — | 2 | 3.32 | Ashok Park Main | Kirti Nagar | 1435 | 25 kV OHE | |||
| Violet Line (Line 06) | 2010-10-03 | 2017-05-28 | 32 | 43.40 | Kashmere Gate | Escorts Mujesar | 44 trains[34] | 1435 | 25 kV OHE | 5 |
| Airport Express (Orange Line) | 2011-02-23 | — | 6 | 22.70 | New Delhi | Dwarka Sector 21 | 8 trains | 1435 | 25 kV OHE | 10 |
| Magenta line (Line 08) | 2017-12-25 | — | 9 | 12.64 | Botanical garden | Kalkaji Mandir | 12 trains[35] | 1435 | 25 kV OHE | 10 |
| Pink line (Line 07) | 2018-03-14 | — | 12 | 21.56 | Majlis Park | Durgabai Deshmukh South Campus | 19 trains[36] | 1435 | 25 kV OHE | 5 |
| TOTAL | 185[1] | 251.74 | ||||||||
Red Line[edit]
The Red Line was the first line of the Metro to be opened and connects Rithala in the west to Dilshad Garden in the east, covering a distance of 25.09 kilometres (15.59 mi).[37] It is partly elevated and partly at grade and crosses the Yamuna River between Kashmere Gate and Shastri Park stations.[38] The inauguration of the first stretch between Shahdara and Tis Hazari on 24 December 2002 caused the ticketing system to collapse due to the line being crowded to four times its capacity by citizens eager to have a ride.[39][40] Subsequent sections were inaugurated from Tis Hazari – Trinagar (later renamed Inderlok) on 4 October 2003,[41] Inderlok – Rithala on 31 March 2004, and Shahdara – Dilshad Garden on 4 June 2008.[42] The red line has two interchange stations, the first Kashmere Gate with the Yellow Line and Violet Line and the second Inderlok with the Green Line. Beginning 24 November 2013, a total of six-coach trains were eventually commissioned on the Red Line.[43]
Yellow Line[edit]
The Yellow Line was the second line of the Metro and was the first underground line to be opened on the Delhi Metro.[44] It runs for 49 kilometres (30 mi) from north to south and connects Samaypur Badli with HUDA City Centre in Gurgaon. The northern and southern parts of the line are elevated, while the central section which passes through some of the most congested parts of Delhi is underground. The first section between Vishwa Vidyalaya and Kashmere Gate opened on 20 December 2004, and the subsequent sections of Kashmere Gate – Central Secretariat opened on 3 July 2005, and Vishwa Vidyalaya – Jahangirpuri on 4 February 2009.[42] This line also possesses the country’s deepest Metro station[45] at Chawri Bazaar, situated 25 metres (82 ft) below ground level.[46]
On 21 June 2010, an additional stretch from Qutub Minar to HUDA City Centre was opened, initially operating separately from the mainline. However, Chhatarpur station on this line opened on 26 August 2010. Due to delays in acquiring the land for constructing the station, it was constructed using prefabricated structures in a record time of nine months and is the only station in the Delhi Metro network to be made completely of steel.[47][48] The connecting link between Central Secretariat and Qutub Minar opened on 3 September 2010.[49]
On 10 November 2015, the line was further extended between Jahangirpuri and Samaypur Badli in Outer Delhi.[50] Interchanges are available with the Red Line and Kashmere Gate ISBT at Kashmere Gate station, Blue Line at Rajiv Chowk Station, Violet Line at Central Secretariat, Airport Express (Orange) Line at New Delhi, Rapid Metro Gurgaon at Sikandarpur and with the Indian Railways network at Chandni Chowk and New Delhi.[51][52]
The yellow line is the first line of Delhi Metro which has phased out all four coach trains with six and eight coach configuration. The Metro Museum at Patel Chowk Metro station is a collection of display panels, historical photographs and exhibits, tracing the genesis of the Delhi Metro. The museum was opened on 1 January 2009.[45]
Blue Line[edit]
The Blue Line was the third line of the Metro to be opened and the first to connect areas outside Delhi.[53] Mainly elevated and partly underground,[54] it connects Dwarka Sub City in the west with the satellite city of Noida in the east, covering a distance of 47.4 kilometres (29.5 mi).[53] The first section of this line between Dwarka and Barakhamba Road was inaugurated on 31 December 2005, and subsequent sections opened between Dwarka – Dwarka Sector 9 on 1 April 2006, Barakhamba Road – Indraprastha on 11 November 2006, Indraprastha – Yamuna Bank on 10 May 2009, Yamuna Bank – Noida City Centre on 12 November 2009, and Dwarka Sector 9 – Dwarka Sector 21 on 30 October 2010.[42] This line crosses the Yamuna River between Indraprastha and Yamuna Bank stations,[38] and has India’s second extradosed bridge across the Northern Railways mainlines near Pragati Maidan.[55]
A branch of the Blue line, inaugurated on 8 January 2010, takes off from Yamuna Bank station and runs for 6.25 kilometres (3.88 mi) up to Anand Vihar in east Delhi.[56] It was further extended up to Vaishali which was opened to the public on 14 July 2011.[57] A small stretch of 2.76 kilometres (1.71 mi) from Dwarka Sector 9 to Dwarka Sector 21 was inaugurated on 30 October 2010.[58] Interchanges are available with the Yellow Line at Rajiv Chowk station,[54] Green line at Kirti Nagar, Violet line at Mandi House, Airport Express (Orange) line at Dwarka Sector 21 and with the Indian Railways network and Interstate Bus Station (ISBT) at Anand Vihar station, which connects with Anand Vihar Railway Terminal and Anand Vihar ISBT.[59]
Green Line[edit]
Opened in 2010, Green Line (Line 5) is the fifth line of the Delhi Metro network and the first line on standard gauge, as opposed to previous broad gauge lines. It runs between Inderlok (station on the Red Line) and Mundka with a branch line connecting the line’s Ashok Park Main station with Kirti Nagar station on the Blue Line. The completely elevated line, built as part of the Phase-II of Delhi Metro runs mostly along the busy NH 10 route in West Delhi. The line consists of 17 stations including an interchange station covering a total length of 18.46 km. This line also has the country’s first standard-gauge maintenance depot at Mundka.[60]
The line was opened in two stages, with the 15.1 km Inderlok – Mundka section opening on 3 April 2010 and the 3.5 km Kirti Nagar – Ashok Park Main branch line on 27 August 2011. On 6 August 2012, in a step that will improve commuting in National Capital Region, the Union Government approved an extension of Delhi Metro from Mundka to Bahadurgarh in Haryana. The 11.18 km metro stretch will have seven stations at Mundka Industrial Area, Ghevra, Tikri Kalan, Tikri Border, Modern Industrial Estate, Bahadurgarh Bus Stand and City Parkbetween Mundka and Bahadurgarh.
Violet Line[edit]
The Violet Line is the sixth line of the Metro to be opened, and the second standard-gauge corridor after the Green Line. The 40-kilometre-long (25 mi) line connects Escorts Mujesar in Faridabad to Kashmere Gate in New Delhi, with 22.8 km (14.2 mi) being overhead and the rest underground. The first section between Central Secretariat and Sarita Vihar was inaugurated on 3 October 2010, just hours before the inaugural ceremony of the 2010 Commonwealth Games, and connects the Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium, which was the venue for the opening and closing ceremonies of the event.[61] Completed in just 41 months, it includes a 100-metre-long (330 ft) bridge over the Indian Railways mainlines and a 167.5-metre-long (550 ft) cable-stayed bridge across an operational road flyover and connects several hospitals, tourist attractions, and a major industrial estate along its route. Services are provided at intervals of 5 min.[61][62] An interchange with the Yellow Line is available at Central Secretariat through an integrated concourse. On 14 January 2011, the remaining portion from Sarita Vihar to Badarpur was opened for commercial service, adding three new stations to the network and marking the completion of the line.[63]
The section between Mandi House and Central Secretariat, was opened on 26 June 2014. After that, a 971-metre section between ITO and Mandi House was opened on 8 June 2015. The latest addition to the line, a 14 km (8.7 mi) extension southwards till Escorts Mujesar in Faridabad was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on 6 September 2015.[64] All the nine Metro stations of the Badarpur – Escorts Mujesar (Faridabad) section of Delhi Metro’s Phase 3, have been awarded the highest possible rating (platinum) for adherence to green building norms, by the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC), which has devised a rating mechanism for Metro stations and buildings on a scale of platinum, gold, silver etc. for following the green building specifications. The awards for these stations were given to DMRC’s Managing Director, Dr. Mangu Singh by Dr. P C Jain, Chairperson, IGBC in the presence of DMRC’s directors and senior officials on 10 September 2015.[65]
Currently, the Faridabad corridor of Delhi Metro Violet Line is the longest metro corridor outside of Delhi, consisting of 9 stations and the total length of corridor being 14 km.[66] On 28 May 2017, the ITO – Kashmere Gate corridor of the Delhi Metro was formally flagged off for passenger services by the Union Minister of Urban Development, M. Venkaiah Naidu and the Chief Minister of Delhi, Arvind Kejriwal. This section which runs underground is popularly known as the Heritage Line.[67]
Orange Line: Airport Express[edit]
The Airport Express line runs for 22.7 km (14.1 mi) from New Delhi Railway Station to Dwarka Sector 21, linking the Indira Gandhi International Airport. The line was operated by Delhi Airport Metro Express Pvt. Limited (DAMEL), a subsidiary of Reliance Infrastructure, the concessionaire of the line till 30 June 2013 and is now being operated by DMRC.[68] The line was constructed at a cost of ₹57 billion(US$870 million), of which Reliance Infrastructure invested ₹28.85 billion (US$440 million) and will pay fees on a revenue-share model.[69]The line has six stations (Dhaula Kuan and Delhi Aerocity became operational on 15 August 2011), with some featuring check-in facilities, parking, and eateries.[70] Rolling stock consists of six-coach trains operating at intervals of ten minutes and having a maximum speed of 135 km/h (84 mph).[70]
Originally scheduled to open before the 2010 Commonwealth Games, the line failed to obtain the mandatory safety clearance and was opened on 24 February 2011, after a delay of around 5 months. After 16 months of commencement of operations, the line was shut down for repairs of the viaducts on 8 July 2012.[71][72] The line reopened on 22 January 2013.[73] On 27 June 2013 Reliance Infrastructure Ltd intimated DMRC that they are unable to operate the line beyond 30 June 2013. Following this DMRC took over operations of Airport Express line from 1 July 2013 with an Operations and Maintenance team of 100 officials to handle the line.[74] In Jan 2015, DMRC reported that Airport Metro has recorded about 30 percent rise in its ridership following the fare reduction of up to 40 percent in July last year[75] On 14 September 2015 DMRC announced to reduce fares even further to improve the ridership of the line, the new fare structure will have maximum fare of ₹60 and minimum of ₹10 instead of ₹100 and ₹20 charged earlier, a reduction of about 40%.[76] DMRC has stated that this was done to reduce the crowding on Blue line, diverting some of the Dwarka-bound passengers to Airport Express Line, which is underutilised and faster compared to the Blue Line.
Phase III[edit]
Phase-I (Red, Yellow and Blue lines) and phase-II (Green, Violet and Orange lines) had focused on adding new radial lines to expand the network. To reduce the congestion and improve the connectivity, Phase-III includes 11 extensions to the existing lines as well as building two ring lines (Pink and Magenta lines). Phase-III has 28 underground stations, 2 new lines and 11 route extensions, totalling 167.27 km, with a cost of ₹350 billion (US$5.4 billion).[77] Phase 3 contains 3 new Lines in Delhi Metro System, Pink Line running on Inner Ring Road (Line 7), Magenta Line running on Outer Ring Road (Line 8) & Gray Line connecting Dwarka and Najafgarh (Line 09).
Work on Phase III started in 2011,[78][79] with 2016 being the planned deadline,[80] more than 20 tunnel boring machines were used simultaneously to expedite the work,[81] however, the actual work is planned to be completed by end of 2018, subject to availability of land in certain pockets.[82]
Kalkaji Mandir to Botanical Garden section of Magenta Line was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Christmas 2017, making it the first driverless line of Delhi Metro.[83] Port Island Line in Kobe (Japan) was one of the world’s first automated urban metro subway systems.
The expected daily ridership of the whole network of all phases, after the completion of Phase-III, is 4 million passengers. The communication-based train control (CBTC) is being used in Phase-III trains which enables trains to run at a short headway of 90 seconds.[84] Keeping this in mind and other constraints, DMRC changed its decision to build 9-car-long stations for new lines and instead opting for shorter stations which can accommodate 6-car trains.
Phase-III lines are:
| Line | Stations | Length (km) |
Terminals | No. of Interchanges Planned |
Expected Date of Completion[80] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow Line extension (Line 02) | 3 | 4.37 | Jahangirpuri | Samaypur Badli | 0 | Completed |
| Violet Line extension (Line 06) | 7 | 9.37 | Central Secretariat | Kashmere Gate | 3 | Completed |
| 11 | 17.075 | Badarpur | Ballabhgarh | 0 | June 2018 (Partially Completed till Escorts Mujesar) | |
| Gray Line (Line 09) | 4 | 4.295 | Dwarka | Dhansa Bus Stand | 1 | December 2018 |
| Blue Line extension (Line 03) | 6 | 6.675 | Noida City Centre | Noida Electronic City | 1 | April 2018 |
| Green Line extension (Line 05) | 7 | 11.182 | Mundka | Bahadurgarh City Park | 0 | April 2018 |
| Pink Line also called Inner Ring Road Line (Line 7)[85] | 12 | 21.56 | Majlis Park | Durgabai Deshmukh South Campus | 5 | Completed |
| 26 | 37.05 | Durgabai Deshmukh South Campus | Shiv Vihar | 6 | June 2018 | |
| Magenta Line also called Outer Ring Road Line (Line 8) | 9 | 12.64 | Kalkaji Mandir | Botanical Garden | 2 | Completed |
| 16 | 25.595 | Janakpuri West | Kalkaji Mandir | 2 | June 2018 | |
| Red Line extension (Line 01) | 6 | 9.41 | Dilshad Garden | New Bus Adda | 0 | June 2018 |
| Delhi Airport Metro Express extension (Line 06) | ? | 1.878 | Dwarka sector 21 | ECC Centre | 0 | |
| Aqua Line Noida-Greater Noida Metro (Not owned by DMRC) – owned and operated by Noida Metro Rail Corporation | 22 | 29.7 | Noida City Centre | Depot Station | 1 | March 2018 |
| Total | 103 | 156.317 | 18 | |||
Magenta Line[edit]
The Magenta Line is the first new line of the Third Phase of the Delhi Metro that was partially opened on 25 December 2017. Currently, the line is opened between Botanical Garden and Kalkaji Mandir.
When complete, it will consist of 25 metro stations from Janakpuri West to Botanical Garden. The Magenta Line will provide direct connectivity to Terminal 1D of Indira Gandhi International Airport. The upcoming Hauz Khas station on this line and the current Yellow Line will be the deepest Metro station at a depth of 29 metres, surpassing the record set by Chawri Bazaar station currently on the Yellow Line, at a depth of 22 metres. The Magenta line has planned interchanges with the Yellow, Blue, and the Violet lines of the Delhi Metro network.
Pink Line[edit]
The Pink Line is the second new line of the Third Phase of the Delhi Metro that was partially opened on 14 March 2018. Currently, the line is opened between Majlis Park to Durgabai Deshmukh South Campus.
It consists of 38 metro stations from Majlis Park to Shiv Vihar, both in North Delhi. Upon completion, the Pink Line with a length of 58.59 kilometres (36.41 mi), will be the longest line in Delhi Metro, breaking the record set by the operational Blue Line. It will be mostly elevated and will cover Delhi in an almost ‘U’ shaped pattern. The Pink Line is also known as the Ring Road Line, as the entire line passes alongside the busy Ring Road in Delhi, that witnesses massive traffic jams everyday.
The Pink line has planned interchanges with most of the operational lines of the network such as the Yellow, Red, Blue, Orange Line and Violet lines, as well as with Hazrat Nizamuddin and Anand Vihar Terminal (Indian Railways) and the ISBT‘s at Anand Vihar and Sarai Kale Khan. The Pink Line has the highest point of Delhi Metro at Dhaula Kuan with a height of 23.6 metres, passing over the Dhaula Kuan grade separator flyovers and the Airport Express Line.[86]
Planned Networks[edit]
Delhi Metro was planned to be built in phases spread over around 20 years as with each phase having a target of five years and end of one phase marking the beginning of another. Phase I (65 km), Phase II (125 km) were completed in 2006 and 2011, respectively. Phase III lines are expected to be completed in 2018, a delay of 2 years from the originally planned timeline of 2016. Phase IV (with extensions to the existing Red, Green, Pink and Magenta lines as well the addition of a new Moss Green line) will commence in 2017 and will be completed by 2022, respectively.[78] A final 370 kilometres (230 mi) route length of 230 kilometres (140 mi) (Phase I & II) and 140 kilometres (87 mi) (Phase III) will be added at the completion of Phase I, II and III. Phase IV plan approved by the Delhi Government will add another 103 kilometres (64 mi) between 2017 and 2022. This makes the total existing and approved route length at the end of Phase IV 456 kilometres (283 mi) long.[87][82] As of July 2017, the 29.7 kilometres (18.5 mi) long under-construction Noida-Greater Noida Metro,[88] 4.86 kilometres (3.02 mi) long approved Narela to Kundli (Sonipat) and the independently operated existing 11.7 kilometres (7.3 mi) long Rapid Metro Gurgaonopened in November 2013 (interchanges with the Delhi Metro at Sikandarpur station on Yellow line)[89] add another 46.26 kilometres (28.74 mi) km to the network, bringing the total network length in NCR to 512.26 kilometres (318.30 mi). This figure is likely to go up as more extensions are approved by Delhi Government as part of Phase IV as well with the addition of more metro routes being independently added in NCR by Haryana and Utter Pradesh Governments.
Phase IV[edit]
Phase IV has a 2022 completion deadline.[90][91] In June 2016, the Detailed Project Report (DPR) for the phase-IV was approved. In January 2017, the Delhi Government approved the Phase IV plan. In July 2017, the Delhi cabinet granted the final approval to the INR 50,000 crore (~ US$6.7 billion) plan in July 2017 on a 50:50 equity basis with the union Government. The Phase IV approved by the Delhi cabinet will add 103 kilometres (64 mi) long route within Delhi in the following proposed corridors:[87][82] Since DMRC will complete all the Phase III work within this year, their equipment and personnel will be available and the work will commence on the Phase-IV within 2017, which will still be completed by 2022 as per the original master plan.[87]
- Rithala – Narela: [1]21.73 kilometres (13.50 mi)
- Inderlok – Indraprastha [2] 12.58 kilometres (7.82 mi)
- Tughlakabad – Aerocity 20.20 kilometres (12.55 mi)
- Lajpat Nagar – Chattarpur [3]7.96 kilometres (4.95 mi)
- Janakpuri (west) – RK Ashram 28.92 kilometres (17.97 mi)
- Mukundpur-Maujpur 12.54 kilometres (7.79 mi)
- HUDA city centre – Gurgaon Railway station 29 kilometres (18 mi)
- IFFCO Chowk – Dwarka Sector 21 12.5 kilometres (7.8 mi)
- Gurugram Railway Station – Palam Vihar Sector 23 7 kilometres (4.3 mi)
- Yamuna Bank – Loni Border
- Najafgarh – Narela RED Line
Connections to Haryana[edit]
- Sonipat Metro – extension:
In June 2017, the Government of Haryana’s cabinet approved the investment of INR 968.20 crore (US$150 million), as its share on the 80:20 equity ratio with the union Government, for the 4.86 kilometres (3.02 mi) extension of Delhi Metro from the existing Rithala metro station to Sonipat via Bawana with three elevated stations at Sector 5 of Narela in Delhi, on Delhi border at Kundli Industrial Area and Nathupur Industrial Area in Sonipat, which are planned to be built starting from April 2018 and to be completed by March 2022 as part of the Phase IV.[92] There are plans to further extend this line deeper into the Sonipat city (via Rajiv Gandhi Education City) and beyond to Murthal (Deenbandhu Chhotu Ram University of Science and Technology) in the future. - Bahadurgarh Metro – Green Line extension:
An extension of Green Line from Mundka along the NH 9 will under construction and on schedule to be completed by December 2017 (as of June 2017).[93] - Rohtak Metro – Green Line extension:
An extension of Green Line from Bahadurgarh, proposed only and not yet approved as of July 2017.[94] - Kharkhoda Metro – Red Line extension:
From the existing Rithala metro station to the new stations in Rohini and Bawana industrial area, to Kharkhoda in Haryana, and up to Rohtak via Sisana as the second line to Rohtak. As of July 2017, proposed only and not yet approved. - Jhajjar Metro – Blue Line extension:
from existing Blue line to Najafgarh and Kharkari in Delhi to Badli in Haryana on Jhajjar border (not to be confused with Badli Industrial area of Delhi in Sonipat border) and Jhajjarcity in Haryana. As of July 2017, proposed only and not yet approved.[95] - Dwarka – AIIMS Bhadsa – Farukh Nagar – Gurugram Blue Line extension:
from existing Blue line at Dwarka to AIIMS Jhajjar at Badsha, Farukh Nagar and Gurugram in Haryana. As of July 2017, proposed only and not yet approved.[95] - Dwarka-Gurugram – Blue Line and Orange Line Airport Express extension:
As second connection via Kapashera and Bijwasan on Haryana border.[96] To complete the metro ring around Gurugram, a proposal was prepared in November 2017 for the two missing routes,[97]
(a) for “HUDA City Centre metro station” to Dwarka Sector 21 metro station (via Sector-45, Sector-46, Sector-47, Subhash Chawk, Bahrampur, Hero Honda Cross, Udhyog Vihar-6, Sector-37 Pataudi road, Sector-10 Basai road, Sector-9 Dhankot railway station, Sector-7, HUDA Road, Sector-4/5, Ashok Vihar, Palam Vihar, Palam Vihar Sector-1, Palam Vihar Sector-23, Sector-111, Bijwasan border, Bijwasan railway station and Barthal),
(b) from HUDA City Centre metro station to Gurgaon railway station (via Sector-45, Sector-46, Sector-47, Subhash Chawk, Rajiv Chawk, HUDA road and Sector-4/5). - Gurugram – Manesar Yellow Line extension and Samaypur Badli to Narela:
An extension of existing yellow line at Gurugram to Manesar Industrial township in the west. In May 2017, a joint study by HUDA and Haryana Town and Planning found the proposal to be technically and financially viable and Detailed Project Report is being prepared for the approval.[94] - Dhaula Kuan-Gurugram-Manesar Personal rapid transit, also called Metrino, was initiated in Dec 2017 by the Government of India by inviting fresh expression of interest from the providers.[98]
- Faridabad – Palwal Violet Line extension:
From existing Faridabad city center to Balramgarh (Ballabhgarh) on the southern outskirts of Faridabad, with future extensions to Palwal district headquarters. As of July 2017, proposed only and not yet approved.[94]
Connections to Uttar Pradesh[edit]
Further extensions are planned to Noida and Ghaziabad.
- Noida – Jewar Air Port Blue Line extension:
In May 2017, INR 7,000 crore (US$1.05 billion) 35 kilometres (22 mi) long road-level extension, along the Yamuna Expressway, of the existing Blue line from Noida to Taj International Airport at Jewar (72 kilometres (45 mi) from Indira Gandhi International Airport) is planned by the Yamuna Expressway Industrial Development Authority (YEIDA), which will be completed by 2022, and will be connected to the under-construction 29.7 kilometres (18.5 mi) long Noida-Greater Noida Metro scheduled to complete by mid-2018.[99] Along with completion of Delhi Western Peripheral Expressway and Delhi Western Peripheral Expressway in 2018, NHAI is constructing two bridges across the Yamuna to connect Faridabad with Noida.[100] - Maujpur – Loni Pink Line extension:
The approved Janakpuri-Mukundpur-Maujpur (across the Yamuna) Pink line is also proposed to be extended to Loni area of Ghaziabad. - Vaishali – Mohan Nagar (Ghaziabad)& Noida Sector 62 – Mohan Nagar (Ghaziabad) – Blue Line extension:
Ghaziabad Development Authority is planning to extend Delhi Metro lines deeper into Ghaziabad through an extension of the Blue Line from Vaishali to Mohan Nagar via Prahlad Gari, Vasundhara Sec- 14 and Sahibabad. And from Noida Sector 62 to Sahibabad via Indirapuram.
Routes[edit]
| Line[101] | Stations | Length (km) |
Terminals | No. of interchanges planned |
Expected Date of Completion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Green Line Extension | 10 | 12.58 | Inderlok | Indraprastha | 5 | |
| Moss Green | 16 | 22.20 | Tughlakabad | IGI Terminal 1 | 4 | |
| Moss Green extension | 6 | 7.96 | CHATTARPUR | Lajpat Nagar | 3 | |
| Pink Line also called Inner Ring Road Line (Line 7) | 7 | 12.54 | Majlis Park | Maujpur | 0 | |
| Magenta Line also called Outer Ring Road Line (Line 8) | 26 | 28.92 | Janakpuri West | Ramakrishna Ashram Marg | 9 | |
| Red Line extension (Line 01) | 19 | 26.59 | Rithala | Nathupur | 0 | August 2022[102] |
| Total | 84 | 110.79 | 21 | |||
Phase V[edit]
Former Managing Director of DMRC, Dr. E Sreedharan stated that by the time Phase IV is completed, the city will need Phase V to cope with rising population and transport needs.[78]
Finances[edit]
Summary financials[edit]
| Fiscal Year ending March | Revenue | Earnings before Interest Taxes Depreciation & Amortization (EBITDA) | Profit Before Tax (PBT) | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | ₹543 crore (equivalent to ₹12 billion or US$180 million in 2017) | ₹399 crore (equivalent to ₹858 crore or US$130 million in 2017) | ₹24 crore (equivalent to ₹52 crore or US$7.9 million in 2017) | [103] |
| 2008 | ₹504 crore (equivalent to ₹10 billion or US$150 million in 2017) | ₹300 crore (equivalent to ₹595 crore or US$91 million in 2017) | ₹26.1 crore (equivalent to ₹52 crore or US$7.9 million in 2017) | [104] |
| 2009 | ₹724 crore (equivalent to ₹13 billion or US$200 million in 2017) | ₹473 crore (equivalent to ₹847 crore or US$130 million in 2017) | ₹90.4 crore (equivalent to ₹144 crore or US$22 million in 2017) | [105] |
| 2010 | ₹738 crore (equivalent to ₹12 billion or US$180 million in 2017) | ₹356 crore (equivalent to ₹569 crore or US$87 million in 2017) | –₹90.2 crore (equivalent to ₹132 crore or US$20 million in 2017) | [106] |
| 2011 | ₹1,608 crore (equivalent to ₹24 billion or US$360 million in 2017) | ₹750 crore (equivalent to ₹11 billion or US$170 million in 2017) | –₹127 crore (equivalent to ₹186 crore or US$29 million in 2017) | [107] |
| 2012 | ₹2,248 crore (equivalent to ₹30 billion or US$460 million in 2017) | ₹933 crore (equivalent to ₹13 billion or US$190 million in 2017) | –₹68.1 crore (equivalent to ₹91 crore or US$14 million in 2017) | [108] |
| 2013 | ₹2,687 crore (equivalent to ₹33 billion or US$500 million in 2017) | ₹1,028 crore (equivalent to ₹12 billion or US$190 million in 2017) | –₹79 crore (equivalent to ₹96 crore or US$15 million in 2017) | [109] |
| 2014 | ₹3,198 crore (equivalent to ₹36 billion or US$560 million in 2017) | ₹1,062 crore (equivalent to ₹12 billion or US$190 million in 2017) | –₹60 crore (equivalent to ₹68 crore or US$10 million in 2017) | [110] |
| 2015 | ₹3,571 crore (equivalent to ₹38 billion or US$590 million in 2017) | ₹1,240 crore (equivalent to ₹13 billion or US$200 million in 2017) | –₹275 crore (equivalent to ₹295 crore or US$45 million in 2017) | [111] |
| 2016 | ₹4,344 crore (equivalent to ₹44 billion or US$680 million in 2017) | ₹1,278 crore (equivalent to ₹13 billion or US$200 million in 2017) | –₹466.6801 crore (equivalent to ₹478 crore or US$73 million in 2017) | [112][113] |
| 2017 | ₹5,387.856 crore (US$830 million) | ₹1,433.0936 crore (US$220 million) | –₹348.1542 crore (US$53 million) | [114] |
Of note, Delhi Metro has been operating with a loss on an EBT basis for the past few years. EBITDA margin declined from 73% in Fiscal 2007 to 29% in Fiscal 2015. That said, Debt to Equity improved from 1.43 in FY07 to 1.22 in FY16.
Funding and capitalisation[edit]
DMRC is owned equally by the Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi and the Government of India.
As of March 2016, total debt stood at ₹291.5 billion (US$4.5 billion), while equity capital was ₹239.9 billion (US$3.7 billion). Cost of the debt is 0% for Union Government and Delhi Government loans and between 0.01% and 2.3% for Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) loans. Of the equity capital as of 31 March 2016, ₹193.1 billion (US$3.0 billion) is paid-up capital and rest is reserves and surplus.[112]
Operations[edit]
The trains operate at a frequency of one to two minutes to five to ten minutes between 05:00 and 00:00, depending upon the peak and off-peak hours. Trains operating within the network typically travel at speed up to 50 km/h (31 mph) and stop for about 20 seconds at each station. Automated station announcements are recorded in Hindi and English. Many stations have services such as ATMs, food outlets, cafés, convenience stores and mobile recharge. Eating, drinking, smoking and chewing gum are prohibited in the entire system. The Metro also has a sophisticated fire alarm system for advance warning in emergencies, and fire retardant material is used in trains as well as on the premises of stations.[115] Navigation information is available on Google Transit.[116] Since October 2010, the first coach of every train is reserved for women. However, last coaches are also reserved when the train changes tracks at the terminal stations in the Red, Green and Violet Lines.[117][118] To make travelling by metro a smoother experience, Delhi Metro has launched its own official app for smartphone users,(iPhone and Android) that will provide information on various facilities like the location of the nearest metro station, fare, parking availability, tourist spots near metro stations, security and emergency helpline numbers.[119]
Security[edit]
Security on the Delhi Metro is handled by the Central Industrial Security Force (CISF), who have been guarding the system ever since they took over from the Delhi Police in 2007.[120] Closed-circuit cameras are used to monitor trains and stations, and feed from these is monitored by both the CISF and Delhi Metro authorities at their respective control rooms.[121] Over 7000 CISF personnel have been deployed for security of metro and its installations in addition to metal detectors, X-ray baggage inspection systems, and dog squads which are used to secure the system. To deal with law and order issues in the system, 18 Delhi Metro Rail Police (A dedicated wing of Delhi Police) stations have been established. About 5,200 CCTV cameras have been installed, which cover every nook and corner of each Metro station. Each of the underground stations has about 45 to 50 cameras installed while the elevated stations have about 16 to 20 cameras each. The monitoring of these cameras is done by the CISF, which is in charge of security of the Metro, as well as the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation.[122]Intercoms are provided in each train car for emergency communication between the passengers and the train operator.[123] Periodic security drills are carried out at stations and on trains to ensure preparedness of security agencies in emergency situations.[124] DMRC is also looking at raising the station walls and railings for the safety of passengers.[125]
Ticketing and recharge[edit]
For the convenience of customers, Delhi Metro commuters have three choices for ticket purchase. The RFID tokens are valid only for a single journey on the day of purchase and the value depends on the distance travelled, with fares for a single journey ranging from ₹10 (15¢ US) to ₹60 (92¢ US). Fares have been revised by DMRC and will be applicable from 10 October 2017. Fares are calculated based on the origin and destination stations using a fare chart.[126] A common ticketing facility for commuters travelling on Delhi Transport Corporation (DTC) buses and the Metro was introduced in 2011.[127] Travel cards are available for longer durations and are most convenient for frequent commuters. They are valid for ten years from the date of purchase or the date of the last recharge and are available in denominations of ₹200 (US$3.10) to ₹2,000(US$30.60). A 10% discount is given on all travel made on it.An additional 10% discount is given to travel card holders for entering the metro system in off-peak hours i.e. From the start of revenue services to 0800 hours, from 1200 hours to 1700 hours and after 2100 hours to end of metro service in the night. This additional discount is given only on Weekdays i.e. from Monday to Saturday.[128] A deposit of ₹50 (77¢ US) needs to be made to buy a new card which is refundable on the return of the card any time before its expiry if the card is not physically damaged.[126] Tourist cards can be used for unlimited travel on the Delhi Metro network over short periods of time. There are two kinds of tourist cards valid for one and three days respectively. The cost of a one-day card is ₹200 (US$3.10) and that of a three-day card is ₹500 (US$7.70), including a refundable deposit of ₹50 (77¢ US) that must be paid at the time of purchasing the card.[126]
Problems[edit]
As the network has expanded, high ridership in new trains has led to increasing instances of overcrowding and delays on the Delhi Metro.[129][130] To alleviate the problem, 8 coach trains have been introduced in Yellow line and Blue line and an increase in the frequency of trains has been proposed.[129] Infrequent, overcrowded and erratic feeder bus services connecting stations to nearby localities have also been reported as an area of concern.[131][132]
Feeder buses[edit]
DMRC operates around 291 feeder buses on 42 routes connecting 54 metro stations in Delhi. Around two lakh people use the feeder bus service on a daily basis.Timings of Feeder Bus operation are 08:00 Hours to 20:00 Hours at a frequency of 10 to 15 minutes depending upon Road Traffic density. However, if an operator wishes he can operate before/beyond these hours. At present Metro Feeder Bus Depots are located at Shastri Park, Kohat Enclave, Janakpuri West, Dwarka Sector-9, Chhatarpur, Yamuna Bank, Azadpur.
Ridership[edit]
Delhi Metro has been registering a continuous increase in ridership since its inception. When Metro services were introduced in 2002, the average ridership was 80,000 passengers per day. As of FY 2016–17, average daily ridership has risen to 2.76 million, with the latest daily ridership record set on 17 August 2016.
Most recent Delhi Metro daily ridership record of 3.3 million passengers was reached on the eve of the Rakshabandhan (17 August 2016), when commuters poured in large numbers throughout the day.[133]
On 25 December 2014, it was reported that the ridership of the Airport Express had almost doubled in the past year to almost 600,000 passengers per month now, as compared to just above 300,000 at the beginning of the calendar year.[134]
Currently, Delhi Metro has about 220 trains of four, six and eight coaches totalling 1,290 coaches. It is further planning to add 421 more coaches on the existing route before the completion of phase 3. During the financial year 2015, DMRC on an average pressed 1,083 coaches in an hour (during peak hour), in 2012–13, the number was 819. On an average, trains make 2,880 trips per day.[135]
| Year | Ridership |
|---|---|
| 2004–05 |
124,000 |
| 2005–06 |
268,000 |
| 2006–07 |
484,000 |
| 2007–08 |
625,000 |
| 2008–09 |
722,000 |
| 2009–10 |
919,000 |
| 2010–11 |
1,259,000 |
| 2011–12 |
1,660,000 |
| 2012–13 |
1,926,000 |
| 2013–14 |
2,190,000 |
| 2014–15 |
2,386,000 |
| 2015–16 |
2,590,000 |
| 2016–17 |
2,760,000 |
Delhi Metro snapshot[edit]
 |
Delhi Metro | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stations | Length (km) | Ridership millions | No. of lines | Revenue | |
| 184 | 251.74 | 1001 | 8 | ₹5,387.856 crore (US$830 million)[114] | |
| Ranking | |||||
| India | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Asia | 6 | 7 | 10 | 9 | |
| World | 11 | 12 | 16 | 13 | |
Rolling stock[edit]
A Phase I broad gauge train, supplied by Hyundai Rotem–BEML.[138]
A Phase II broad gauge train, supplied by Bombardier.
The Metro uses rolling stock of two different gauges. Phase I lines use 1,676 mm (5.499 ft) broad gauge rolling stock, while three Phase II lines use 1,435 mm (4.708 ft) standard gauge rolling stock.[139] Trains are maintained at seven depots at Khyber Pass and Sultanpur for the Yellow Line, Mundka for the Green Line, Najafgarh and Yamuna Bank for the Blue Line, Shastri Park for the Red Line, and Sarita Vihar for the Violet Line.[140][141]
Maglev trains were initially considered for some lines of Phase 3, but DMRC decided to continue with conventional rail in August 2012.[142]
As on 31 March 2015, the Company has a total of 1306 coaches (220 trains). Apart from extensions on various existing lines, two new lines viz. Line 7 & 8 are proposed in Phase III. 486 coaches (81 six-car trains) being procured for these two new lines will have an advance feature in Unattended Train Operation (UTO). Additional 258 Broad gauge (BG) coaches for Line 1 to 4 and 138 Standard Gauge (SG) coaches for Line 5 & 6 are proposed to be procured for augmentation/extensions to cater to the increased traffic. Resultantly, at the end of Phase III, there would be 2188 coaches (333 trains). Barring a few 4-car trains on Line 5, 93% of the trains would operate either in 6 car or 8 car configuration at the end of Phase III.[137]
Broad gauge[edit]
The rolling stock is manufactured by two major suppliers. For the Phase I, the rolling stock was supplied by a consortium of companies comprising Hyundai Rotem, Mitsubishi Corporation, and MELCO. The coaches have a very similar look to MTR Rotem EMU, except with only 4 doors and use sliding doors. The coaches were initially built in South Korea by ROTEM,[141] then in Bangalore by BEML through a technology transfer arrangement.[143] These trains consist of four 3.2-metre-wide (10 ft) stainless steel lightweight coaches with vestibules permitting movement throughout their length and can carry up to 1500 passengers,[144] with 50 seated and 330 standing passengers per coach.[145] The coaches are fully air-conditioned, equipped with automatic doors, microprocessor-controlled brakes and secondary air suspension,[146] and are capable of maintaining an average speed of 32 km/h (20 mph) over a distance of 1.1 km (0.68 mi).[145] The system is extensible up to eight coaches, and platforms have been designed accordingly.[144]
The rolling stock for Phase II is being supplied by Bombardier Transportation, which has received an order for 614 cars worth approximately US$1.1 billion.[147] While initial trains were made in Görlitz, Germany and Sweden, the remainder will be built at Bombardier’s factory in Savli, near Vadodara.[148] These trains are a mix of four-car and six-car consists, capable of accommodating 1178 and 1792 commuters per train respectively. The coaches possess several improved features like Closed Circuit Television (CCTV) cameras with eight-hour backup for added security, charging points in all coaches for cell phones and laptops, improved air conditioning to provide a temperature of 25 °C (77 °F) even in packed conditions and heaters for winter.[149]
Standard gauge[edit]
The standard gauge rolling stock is manufactured by BEML at its factory in Bangalore. The trains are four-car consists with a capacity of 1506 commuters per train,[150]accommodating 50 seated and 292 standing passengers in each coach.[145] These trains will have CCTV cameras in and outside the coaches, power supply connections inside coaches to charge mobiles and laptops, better humidity control, microprocessor-controlled disc brakes,[151] and will be capable of maintaining an average speed of 34 km/h (21 mph) over a distance of 1.1 km (0.68 mi).[145]
Airport Express[edit]
Eight 6-car trains supplied by CAF Beasain were imported from Spain.[152] CAF held 5% equity in the DAME project, and Reliance Infrastructure held the remaining 95%[153] before DMRC took over the operations. The trains on this line are of a premium standard compared to the existing metro trains and have inbuilt noise reduction and padded fabric seats. The coaches are equipped with LCD screens for the entertainment of the passengers and also provide flight information for the convenience of air travellers. The trains are fitted with an event recorder which can withstand high levels of temperature and impact and the wheels have flange lubrication system for less noise and better riding comfort.[117]
Signalling and telecommunication[edit]
Inside a Hyundai Rotem coach.
The Delhi Metro uses cab signalling along with a centralised automatic train control system consisting of automatic operation, protection and signalling modules.[154] A 380 MHz digital trunked TETRA radio communication system from Motorola is used on all lines to carry both voice and data information.[155] For Blue Line Siemens Transportation Systems has supplied the electronic interlocking Sicas, the operation control system Vicos OC 500 and the automation control system LZB 700 M.[156] An integrated system comprising optical fibre cable, on-train radio, CCTV, and a centralised clock and public address system is used for telecommunication during train operations as well as emergencies.[157]For Red and Yellow lines ALSTOM has supplied signalling system and for Green and Violet lines, Bombardier Transportation has supplied CITYFLO 350 signalling system.
The Airport Express line has introduced WiFi services at all stations along the route on 13 January 2012.[158] Connectivity inside metro trains travelling on the route is expected in the future. The WiFi service is provided by YOU Broadband and Cable India Limited.[159]
A fully automated, operatorless train system has been offered to Delhi Metro by the French defence and civilian technologies major Thales.[160]
Environment and aesthetics[edit]
The Delhi Metro has won awards for environmentally friendly practices from organisations including the United Nations,[161] RINA,[162] and the International Organization for Standardization,[162] becoming the second metro in the world, after the New York City Subway, to be ISO 14001 certified for environmentally friendly construction.[163] Most of the Metro stations on the Blue Line conduct rainwater harvesting as an environmental protection measure.[164] It is also the first railway project in the world to earn carbon credits after being registered with the United Nations under the Clean Development Mechanism,[165] and has so far earned 400,000 carbon credits by saving energy through the use of regenerative braking systems on its trains.[166] To reduce its dependence on non-renewable sources of energy, DMRC is looking forward to harnessing solar energy and install solar panels at the Karkardooma, Noida Sector-21, Anand Vihar and Pragati Maidan Metro stations and DMRC’s residential complex at Pushp Vihar.[167][168] As of March 2017, the DMRC has commissioned 20 MWp (megawatt peak) of solar power plants across 21 locations on the metro network. This is planned to increase to 31 MWp by March 2018, and 50 MWp by 2021.[169]
The Metro has been promoted as an integral part of community infrastructure, and community artwork depicting the local way of life has been put on display at stations.[170] Students of local art colleges have also designed decorative murals at Metro stations,[171] while pillars of the viaduct on some elevated sections have been decorated with mosaic murals created by local schoolchildren.[172] The Metro station at INA Colony has a gallery showcasing artwork and handicrafts from across India,[173] while all stations on the Central Secretariat – Qutub Minar section of the Yellow Line have panels installed on the monumental architectural heritage of Delhi.[174] The Nobel Memorial Wall at Rajiv Chowk has portraits of the seven Nobel Laureates from India: Rabindranath Tagore, CV Raman, Hargobind Khorana, Mother Teresa, Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar, Amartya Sen and Venkatraman Ramakrishnan and provide details about their contribution to society and a panel each on Alfred Nobel and the Nobel Prizes.
LINK/INFORMATION COURTESY: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Delhi_Metro